In November 2023 the International Telecommunication Union’s Radiocommunication sector (ITU-R) reached a consensus on the global vision for IMT-2030 (6G), which is expected to be a fundamental milestone in developing 6G. Notably, the ITU’s consultation process included countries all around the world. While there has been some concern that geopolitical pressures would create a de facto split in standards, work is ongoing to avoid this. It is extremely rare to find anyone within the telecoms community advocating for anything other than globally unified technical standards.
The published Framework, approved by the ITU Radiocommunication Assembly (RA-23) in November 2023, outlines some key vision areas, such as capabilities and use cases, which we will explain in this article.
What Is ITU’s Vision For A Global 6G Standard?
4G’s arrival equipped us with more access to social engagement. 5G enabled us to leverage data from machines and sensors. The sixth generation is expected to combine physical and digital worlds to transform how we live, communicate, and work.
Doreen Bogdan-Martin, ITU Secretary-General, said: “Mobile communications are central to our efforts to ensure that everyone is meaningfully connected.”
“By agreeing on a way forward on 6G, ITU Member States have taken an important step toward ensuring that technical progress is synonymous with affordability, security, and resilience — supporting sustainable development and digital transformation everywhere.”
6G Capabilities
Here are the expected capabilities and use cases of 6G, as outlined in the IMT-2023 Framework:
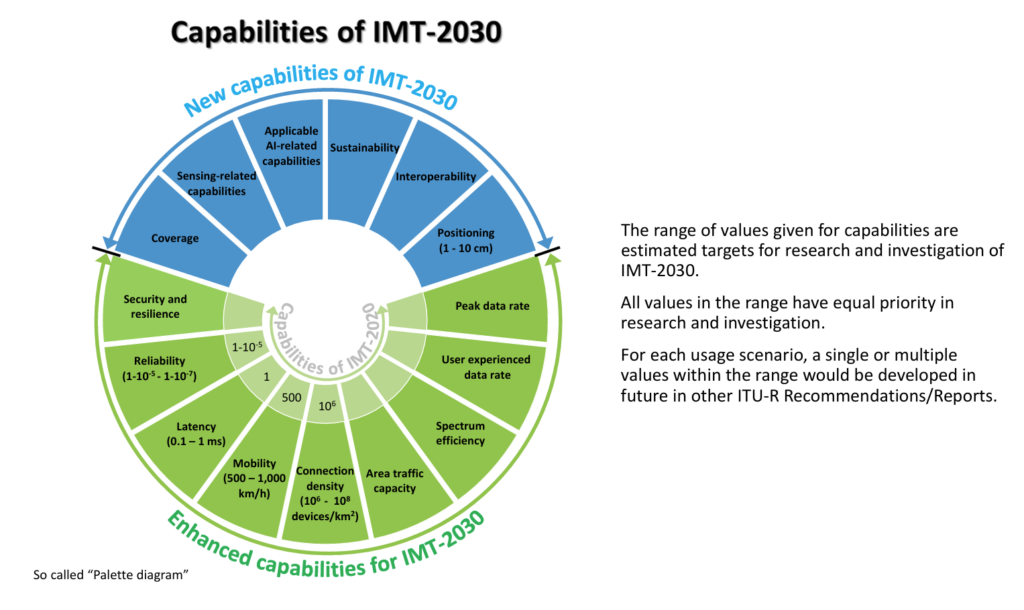
The IMT-2030 Framework identifies 15 capabilities for 6G technology, nine of which will be enhanced from existing 5G capabilities, including security and resilience, latency, mobility, connection density, peak data rate, and spectrum efficiency.
Here are the six brand-new capabilities:
- Coverage: The ability to provide access to communication services for users in a desired service area. Previously coverage was not built into standards but a function of the regulatory regime of different countries.
- Sustainability: 6G and devices such as smartphones and tablets will minimise greenhouse gas emissions and the other environmental impacts of their life cycle.
- Sensing-related capabilities: This refers to the ability to provide functionality through the radio signal, including object detection, localisation, imaging, and mapping.
- Applicable artificial intelligence (AI)-related capabilities: AI-based capabilities can support applications, including distributed data processing, distributed learning, computing, and model execution and inference. They can also optimise and automate existing network functions.
- Interoperability: This refers to the radio interface being based on member inclusivity and transparency.
- Positioning: The ability to calculate the approximate position of connected devices. The positioning accuracy is defined as the difference between the calculated horizontal/vertical position and the actual horizontal/vertical position of a device.
 (Image Source: ITU)
(Image Source: ITU)6G Use Cases
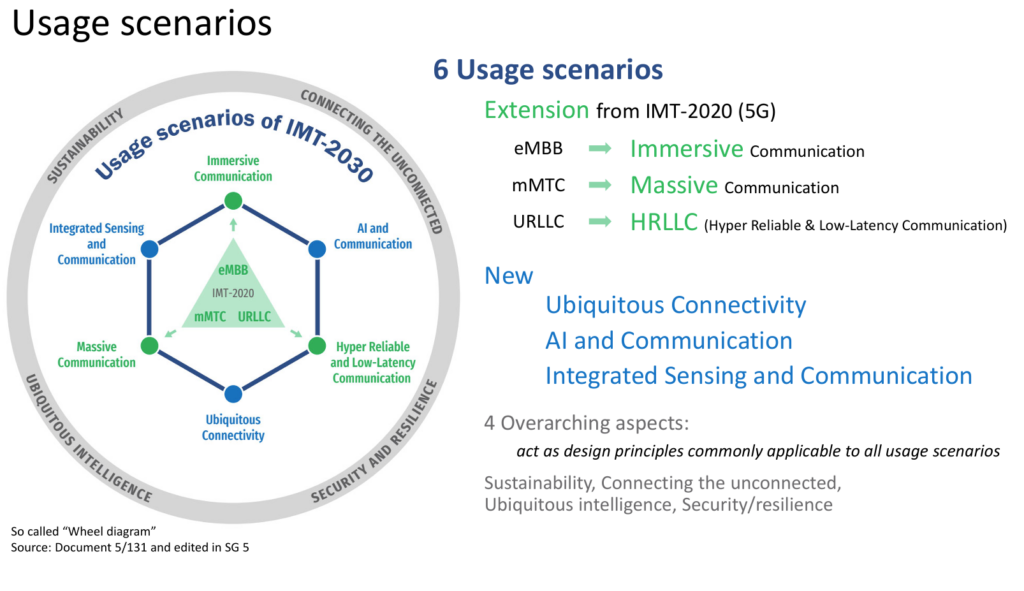
Usage scenarios of IMT-2030 will expand on those of IMT-2020. In addition, it will also enable new use cases arising from 6G capabilities, such as AI and sensing, which previous generations of IMT were not designed to support.
The usage scenarios of IMT-2030 include:
- Immersive communication: This will provide users with a rich and interactive video experience, including interactions with machine interfaces. Typical use cases include communication for immersive XR, remote multi-sensory telepresence, and holographic communications. While 5G is theoretically also capable of supporting these use cases, the numbers supported by a single cell are very limited, so this is an extension of those capabilities.
- Hyper-reliable and low-latency communication: This will enhance communications in an industrial environment for full automation, control, and operation. These types of communications can help various applications such as machine interactions, emergency services, telemedicine, and monitoring for electrical power transmission and distribution. This is an extension of 5G’s URLLC.
- Ubiquitous connectivity: This will bridge the digital divide, especially for rural and remote areas. Typical use cases include IoT and mobile broadband communication but can also include access for hikers, farmers and others.
- Massive communication: This will connect many devices or sensors for various use cases and applications, including in smart cities, transportation, logistics, health, energy, environmental monitoring, and agriculture. This, too, is an extension of what has been defined in 5G.
- AI and communication: This will support automated driving, autonomous collaboration between devices for medical assistance applications, offloading heavy computation operations across devices and networks, creation of and prediction with digital twins, and more.
- Integrated sensing and communication: This will improve applications and services requiring sensing capabilities, such as assisted navigation, activity detection, movement tracking, environmental monitoring, and sensing data on surroundings for AI and XR.

(Image Source: ITU)
What Is The ITU’s Timeline For Creating A Global 6G Standard?
The successful completion of the IMT-2030 Framework marks the official start of the journey toward global 6G standardisation. 6G will be implemented through global cooperation following the timeline set by ITU-R:

What Else Is Outlined In The Global Vision For 2030 And Beyond?
The Recommendation for IMT-2030 is also expected to address the need for increased environmental, social, and economic sustainability, and support the goals of the Paris Agreement.
This 2015 agreement aims to combat climate change and advance the actions and investments needed for a sustainable, low-carbon future.
Article contributed by Neve Wilkinson, title image by ResoneTIC